
How to file income tax in Singapore
Singapore operates on a territorial tax system, meaning that individuals and businesses are taxed only on income earned within Singapore. The tax rates vary based on income brackets for individuals and corporate profits for businesses. To file income tax in Singapore, taxpayers must report all relevant earnings and apply any eligible deductions. The e-filing IRAS Singapore portal simplifies this process, ensuring efficient and paperless tax submission.
A key concept in taxation is estimated chargeable income, which refers to the projected taxable income of a business. Companies must declare their estimated chargeable income in Singapore to the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) within three months of the financial year-end.
Filing income tax in Singapore is a crucial responsibility for individuals and businesses. With the e-filing IRAS Singapore system, taxpayers can efficiently submit their income tax returns while ensuring compliance with the country's regulations. Understanding estimated chargeable income in Singapore is essential for accurate tax assessment and filing. In this blog, we will cover everything you need to know about how to file income tax in Singapore efficiently.
Who Needs to File Income Tax in Singapore?
Both individuals and companies must file income tax in Singapore if they meet certain criteria:
- Individuals: Anyone earning more than SGD 22,000 annually must file taxes through e-filing IRAS Singapore portal.
- Companies: All registered companies must submit their estimated chargeable income in Singapore and corporate tax returns.
- Self-Employed/Freelancers: Individuals earning income outside of employment contracts must report their earnings.
IRAS provides e-filing services to streamline the tax submission process for all taxpayers.
Types of Income Tax Filings in Singapore
When you file income tax in Singapore, you need to know the different tax filing types:
- Personal Income Tax: Individuals report their employment or self-employed earnings.
- Corporate Income Tax: Businesses declare their estimated chargeable income in Singapore and final tax obligations.
- Withholding Tax: Applied to foreign companies or individuals earning income from Singapore sources.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): Required for businesses with annual revenue exceeding SGD 1 million.
For all these tax types, e-filing IRAS Singapore is the preferred method of submission.
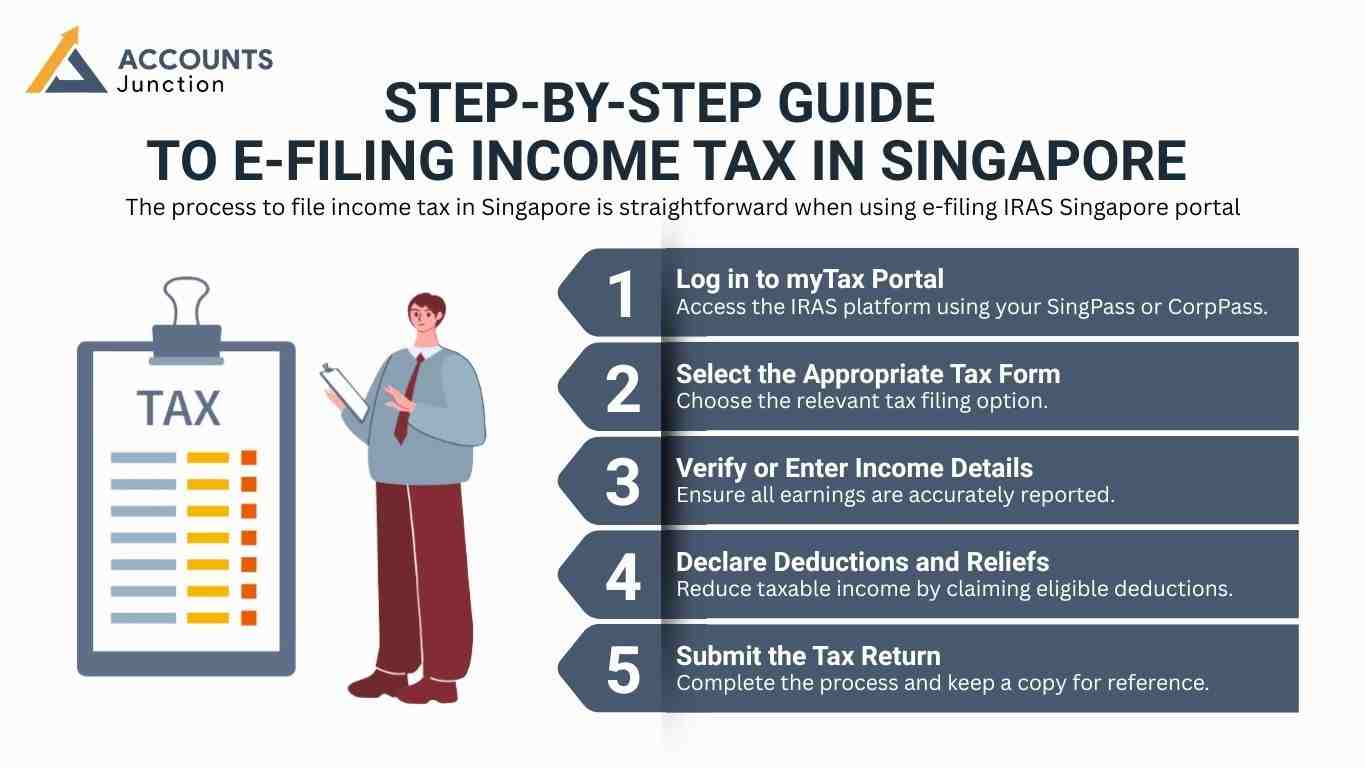
Step-by-Step Guide to E-Filing Income Tax in Singapore
The process to file income tax in Singapore is straightforward when using e-filing IRAS Singapore portal:
- Log in to myTax Portal: Access the IRAS platform using your SingPass or CorpPass.
- Select the Appropriate Tax Form: Choose the relevant tax filing option.
- Verify or Enter Income Details: Ensure all earnings are accurately reported.
- Declare Deductions and Reliefs: Reduce taxable income by claiming eligible deductions.
- Submit the Tax Return: Complete the process and keep a copy for reference.
Corporate taxpayers must also report their estimated chargeable income in Singapore within three months after the financial year ends.
Registering for E-Filing with IRAS Singapore
To access e-filing IRAS Singapore, you need to register:
- Individuals: Use your SingPass to access the system.
- Businesses: Companies must activate their CorpPass accounts for tax filing.
- Foreigners: Non-residents can register for an IRAS Unique Account (IUA) to file income tax in Singapore.
After registration, you can seamlessly manage tax obligations, including declaring estimated chargeable income in Singapore.
How to Prepare Your Tax Documents
Before using e-filing IRAS Singapore, gather the following documents:
- Form IR8A from your employer (for salaried individuals)
- Income records for self-employed individuals
- Financial statements for businesses declaring estimated chargeable income in Singapore
- Deduction receipts for eligible claims
Organizing these documents ensures a smooth process when you file income tax in Singapore.
Submitting Your Tax Returns via IRAS E-Filing
When using e-filing IRAS Singapore, follow these steps:
- Access myTax Portal: Log in with your credentials.
- Fill Out the Tax Form: Enter income details and tax reliefs.
- Verify the Information: Double-check accuracy before submission.
- Submit Before the Deadline: Ensure you file on time to avoid penalties.
- Receive the Notice of Assessment (NOA): IRAS will confirm your tax obligations after processing.
For corporate taxpayers, estimated chargeable income in Singapore must be declared within the stipulated time frame.
Why Choose Accounts Junction for Filing Income Tax in Singapore?
Accounts Junction provides expert assistance to help businesses and individuals file income tax in Singapore efficiently. With expertise in e-filing IRAS Singapore, our services include:
- Accurate Tax Preparation: Ensuring compliance with Singapore’s tax regulations.
- Timely Submission: Avoid penalties by meeting deadlines for tax filing and estimated chargeable income declaration.
- Personalized Guidance: Expert tax consultation tailored to your financial needs.
- Seamless Integration: Assistance with myTax Portal and IRAS registration.
Choosing Accounts Junction ensures that you file your taxes correctly and optimize tax benefits.
Filing income tax in Singapore is a crucial responsibility for individuals and businesses, ensuring compliance with the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS). E-filing through IRAS Singapore makes the process easier and reduces errors and delays. Staying informed about estimated chargeable income in Singapore and tax filing types is key to meeting regulations.
Taxpayers can easily file taxes by following the guide, from registering for e-filing with IRAS Singapore to submitting returns online. Proper tax document preparation, understanding deductions, and adhering to deadlines are key factors in filing income tax smoothly.
For businesses and individuals looking for expert guidance, Accounts Junction offers professional tax filing services, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and optimized tax planning. Whether you're new to filing or need help with complex taxes, professional support saves time and avoids costly mistakes.
FAQs
1. Who needs to file income tax in Singapore?
- Anyone earning over SGD 22,000 annually, businesses with taxable income, and companies declaring estimated chargeable income in Singapore must file income tax.
2. What is e-filing IRAS Singapore?
- It is the online tax submission system provided by IRAS, allowing individuals and businesses to submit tax returns digitally.
3. When is the deadline for filing income tax in Singapore?
- For individuals, the deadline is April 18 for e-filing IRAS Singapore. For businesses, estimated chargeable income must be submitted within three months of the financial year-end.
4. What happens if I miss the tax filing deadline?
- Submitting late may lead to fines and added interest charges. It is essential to file income tax in Singapore on time.
5. Can I amend my tax return after submission?
- Yes, amendments can be made via e-filing IRAS Singapore before IRAS finalizes your tax assessment.
6. What documents do I need before filing my income tax in Singapore?
- You may need payslips, Form IR8A from your employer, proof of deductions, or business financial records if you are declaring estimated chargeable income in Singapore. Having these ready can make e-filing smoother.
7. How can I check if I need to file a tax return with IRAS Singapore?
- You can log in to your myTax Portal. If IRAS requires you to file, a notice may appear under your messages. Some taxpayers might also get a direct reminder by mail or email.
8. What is the difference between income tax and estimated chargeable income?
- Income tax is based on your total yearly earnings, while estimated chargeable income in Singapore is an early estimate that companies must declare before their final tax return. It helps IRAS project corporate tax in advance.
9. Can foreigners file their taxes using e-filing IRAS Singapore?
- Yes, non-residents can e-file using an IRAS Unique Account (IUA). This allows foreign workers or business owners to meet tax obligations in Singapore.
10. What if I overpaid my income tax?
- If you pay more than you owe, IRAS may refund the extra amount to your bank account or issue a cheque. Refunds are usually processed after your assessment is finalized.
11. How do companies declare their estimated chargeable income in Singapore?
- Businesses log in to myTax Portal using CorpPass, fill in their financial data, and submit the ECI form within three months of their financial year-end. This step helps them stay compliant with IRAS.
12. Can I file my income tax in Singapore without SingPass?
- You need SingPass or CorpPass to access the e-filing IRAS Singapore system. If you do not have one, you can register online or visit the SingPass counters to set it up.
13. What deductions can I claim while filing income tax in Singapore?
- You may claim deductions for work-related expenses, CPF contributions, donations, and certain approved courses. These can lower your taxable income and reduce your tax bill.
14. How can I know my tax payable amount?
- After you e-file, IRAS reviews your submission and sends a Notice of Assessment (NOA). This document shows your total income, tax reliefs, and the final tax payable or refundable amount.
15. What happens if I do not declare my estimated chargeable income in time?
- Late submission might lead to IRAS using its own estimate, which may be higher than your actual income. Penalties may also apply for non-compliance.
16. How do self-employed individuals file income tax in Singapore?
- Freelancers and self-employed persons must report their business income through e-filing IRAS Singapore. They can attach income records and deduct business expenses to find their taxable income.
17. Can I pay my income tax in installments?
- Yes, IRAS allows payment by GIRO instalments. You can apply for this plan through the myTax Portal to spread payments over several months.
18. What if I cannot pay my taxes on time?
- If payment is delayed, IRAS may charge late fees or interest. It is best to contact IRAS early to discuss a payment arrangement and avoid legal action.
19. Are there penalties for wrong tax declarations?
- Yes, giving false or incomplete information might lead to penalties. Always check your details before submitting through e-filing IRAS Singapore.
