
What are accounts payable?
Accounts payable is the practice of managing payable obligations of an enterprise or entity. It is a critical business process in which an amount is owed by the enterprise for supplied services. In simpler terms, an entity orders services or products and gets them before making a prior payment.
This dealing is a recorded liability in the systems of accounts depending on the invoice amount. Accountability due to such suppliers or vendors is called the accounts payable process. Once the liability or due amounts are paid by the entity, it is reduced from their accounts payable balance.
Importance of accounts payable
For the all-around functioning of any business entity, accounts payable and their management play a vital role. Many benefits supporting this are,
-
Helps Control Cash Flow: Firms pay bills only when due, using credit. This helps keep more cash on hand for key needs.
-
Builds Strong Vendor Ties: By paying on time, firms show trust and care. This builds long-term ties with vendors.
-
Keeps Work on Track: Paying bills on time keeps the flow of goods, work, and records smooth and on point.
-
Stops Late Fees: A clear process helps firms avoid missed due dates, fines, and late fees.
-
Cuts Risk of Fraud: Strong checks in the process help find and stop fraud and theft in early stages.
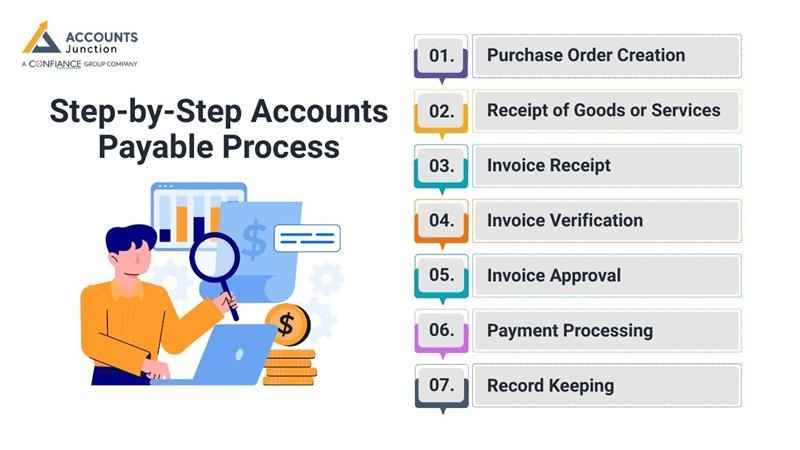
Step-by-Step Accounts Payable Process
1. Purchase Order Creation
- A department requests goods or services.
- A Purchase Order (PO) is issued with item names, counts, and agreed prices.
- The PO is sent to the supplier to confirm the request and terms.
2. Receipt of Goods or Services
- The company receives the items or services.
- Staff check the delivery against the PO for count and quality.
- A Goods Receipt Note (GRN) is issued to acknowledge the receipt of goods.
3. Invoice Receipt
- The supplier sends an invoice after delivery.
- The invoice lists items, costs, and due dates.
- The Accounts Payable (AP) team records the invoice in the system.
4. Invoice Verification
- The invoice is compared with the PO and GRN.
- This step checks that the price, item, and count all agree.
- If errors are found, they are resolved before moving on.
5. Invoice Approval
- The checked invoice is sent to the correct team or manager.
- Approval means the goods or services were received as agreed.
6. Payment Processing
- Once approved, the invoice is set for payment.
- Payment is made by bank, cheque, or digital method.
- On-time payment keeps good ties with the supplier.
7. Record Keeping
- The payment is entered in the company’s books.
- These records support reports, audits, and future needs.
How automation of the accounts payable process help?
To save time, and have an efficient accounts payable process with automation updates is necessary. Moreover, automation immensely helps in reducing human errors and processing the cost of invoices timely manner.
Many accounting software programs are successful in streamlining the accounts payable process for businesses. It eliminates the paperwork accounting job that is strenuous. All the invoice payments are digitally generated and can be scanned, copied, and emailed for approvals. This saves a lot of time, improving the performance of the business. Hence, the automation in the accounts payable process is a clever move.
Accounts payable processing in Xero with receipt bank
A software that is successful in initiating amazing collaboration is Receipt Bank. It is an easy-to-use software that does not need any paperwork. This software is able to extract your accounts payable data and export suitable accounting software. Some of its many advantages are,
- Assemblage accounting services, by making records from invoices, even if payments are due for less confusion.
- Cash management to help during the budget formation periods.
- Features of automated entries and import of data within a time, to ensure accuracy in cash flow in the business.
- Provides an overview of payments and monetary investments, so you can easily forecast future requirements of business transactions.
Common Challenges in Accounts Payable
The accounts payable process can face several issues:
- Invoice Mistakes: Errors in bills, orders, or receipts can cause delays and disputes.
- Human Errors: Typing and data entry mistakes can affect financial records.
- Late Payments: Missing payment deadlines can lead to fees and hurt supplier relationships.
- Fraud Risks: Without proper checks, fake invoices and payments can happen.
Best Practices for Accounts Payable
To manage accounts payable well, follow these key practices:
- Use Automation: Software tools can speed up the process, cut mistakes, and boost efficiency.
- Set Clear Rules: Clear payment rules help ensure everyone follows the same steps.
- Check Accounts Regularly: Compare the accounts payable records with supplier statements to spot any issues early.
- Train Your Team: Teach staff the process so they can work fast and well.
Accounts Payable Metrics to Track
Monitoring accounts payable is not just about paying bills on time. Certain metrics may show how well your system is working and where improvements are needed. Key metrics include:
-
Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)
Measures the average days a company takes to pay its suppliers. Higher DPO may help cash flow, but can affect relationships.
-
Invoice Processing Time
Tracks how long invoices take from receipt to payment. Shorter times may indicate efficient processes.
-
Error Rate
The percentage of invoices that contain mistakes. Lower error rates may suggest better accuracy in the process.
-
Early Payment Discounts Captured
The number of discounts claimed when paying early. Maximizing this may save money for the business.
Tracking these metrics may help firms adjust strategies, improve cash management, and strengthen supplier relations.
Role of Accounts Payable in Financial Planning
Accounts payable does more than handle bills. It can impact overall financial planning and forecasting. For example:
-
Cash Flow Forecasting
Understanding upcoming payments can help predict cash availability and avoid shortages.
-
Budget Planning
AP records may show where most money is spent and suggest areas for cost optimization.
-
Investment Decisions
Knowing payable obligations may affect timing for investments or expansions.
-
Financial Reporting
Accurate AP ensures that balance sheets and profit statements reflect the true financial position of the business.
By aligning accounts payable with financial planning, a business may improve liquidity and make better strategic choices.
Future Trends in Accounts Payable
Accounts payable is evolving fast, especially with technology and finance trends. Some developments businesses may watch include:
-
AI and Machine Learning
Can automate invoice verification, detect errors, and predict late payments.
-
Cloud-Based Solutions
May allow teams to access AP data remotely and collaborate in real-time.
-
Blockchain for Payments
Could ensure secure and transparent supplier transactions in the future.
-
Sustainability Reporting
AP may integrate supplier sustainability data to support eco-friendly financial decisions.
Staying updated with these trends may keep companies competitive and make AP management more efficient and secure.
The accounts payable process is an easy system, which is vital for the cash flow of every company. High-end business corporations that work along daily monetary investments adopt this system to maintain accounts and track their dues.
Ensuring a strong credit and long-term relationship with vendors and companies, it is a trustworthy system. Hence, it is the safest, easiest, and most efficient method of managing payable obligations. At Accounts Junction, we provide services that streamline this process and fit your business needs. We have certified experts to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Partner with us to experience a seamless and reliable accounts payable solution.
FAQs
1. What is accounts payable in simple terms?
- Accounts payable may be the money a company owes suppliers for goods or services received but not yet paid.
2. Why is accounts payable important for businesses?
- It may help manage cash flow, avoid late fees, and maintain strong supplier relationships.
3. How does accounts payable affect cash flow?
- Proper AP management may ensure enough cash is available for bills and day-to-day operations.
4. What documents are essential for accounts payable?
- Invoices, purchase orders, and goods receipt notes are usually required to process payments.
5. Can automating accounts payable save time?
- Yes, automation may reduce manual work, prevent errors, and speed up invoice processing.
6. What is the accounts payable process?
- It may include receiving invoices, verifying them, getting approvals, making payments, and keeping records.
7. How can accounts payable reduce fraud risk?
- By using approval checks, audits, and digital verification, AP may detect and prevent fake invoices.
8. What is three-way matching in accounts payable?
- It compares the purchase order, invoice, and goods receipt to ensure accuracy before payment.
9. Can errors in accounts payable affect financial reporting?
- Yes, mistakes in AP may show incorrect liabilities and distort balance sheets.
10. What are common challenges in accounts payable?
- Late payments, invoice errors, manual entry mistakes, and fraud risks are typical issues.
11. How does accounts payable help build vendor relationships?
- Paying on time and accurately may strengthen trust and encourage long-term partnerships.
12. Can accounts payable software integrate with accounting tools?
- Yes, integration may streamline payments and automatically update financial records.
13. What role does accounts payable play in budgeting?
- It may help forecast cash requirements and guide financial planning for upcoming payments.
14. How does automation improve accounts payable accuracy?
- Automation may capture invoice data precisely, match orders, and flag inconsistencies automatically.
15. What is the impact of delayed accounts payable payments?
- Late payments may incur fines, disrupt supplier trust, and affect business operations.
16. How can accounts payable metrics improve efficiency?
- Tracking invoice processing time, DPO, and error rates may optimize payments and workflow.
17. Can small businesses benefit from accounts payable automation?
- Yes, even smaller firms may reduce errors, save time, and manage cash flow effectively.
18. What is the importance of record-keeping in accounts payable?
- Maintaining records may support audits, reporting, and verification of past transactions.
19. How does accounts payable influence company credit?
- On-time payments may improve vendor credit terms and strengthen overall financial credibility.
20. What future trends may affect accounts payable management?
- AI, cloud solutions, blockchain, and digital invoicing may shape AP processes and efficiency.
