
Understanding US Payroll Tax: A Simple Guide for Employers and Workers
The US Payroll Tax is a key part of the tax system in the United States. It helps fund Social Security, which provides income and health care for retirees and others in need. Both employees and employers are required to pay this tax on wages earned. Knowing how it works can help you plan better and stay within the law. This guide offers a clear and simple way to understand payroll taxes. It also shares tips to help you stay compliant and avoid costly tax problems.
What is US Payroll Tax?
The US Payroll Tax is a tax required by the federal government to fund Social Security. It supports programs such as Social Security and Medicare. Every paycheck in the United States includes this tax. It is split between employers and workers.
The money collected from the Payroll Tax goes to help people who are retired or disabled. It also funds health coverage for older adults. This tax is not just a cost. It is a tool to support programs that many Americans use. The UPayroll Tax makes sure that Social Security and Medicare get the funding they need.
Key Parts of the US Payroll Tax
The US Payroll Tax is made up of two core parts. These are the Social Security tax and the Medicare tax. Together, they form the complete payroll tax system used in the United States.
The Social Security part covers benefits for people who are retired, disabled or have lost a spouse. The money goes into a federal trust, which pays monthly checks to those who qualify.
The Medicare tax, on the other hand, supports health care costs. It provides hospital insurance to people who are 65 or older, as well as younger individuals with certain conditions. Workers contribute 6.2% of their wages to Social Security and 1.45% to Medicare. Employers also match this same amount. For high earners, an extra Medicare tax may apply, which is known as the Additional Medicare Tax.
These parts are not just lines on a pay stub. They are tools that help build strong support systems. Whether you are young or close to retirement, these taxes work to serve everyone.
Knowing these parts helps workers and businesses better plan for the future. The more we understand how payroll taxes function, the better we can manage them.
All About Medicare Taxes
Medicare taxes are one of the main taxes in the US Payroll Tax system. These taxes fund Medicare, a health program mainly for people over 65. Every worker in the US helps fund Medicare through payroll taxes. Employers must also match this amount. For most people, this tax is 1.45% of wages. Workers earning more than $200,000 pay an extra 0.9%. This is the Additional Medicare Tax. It helps cover rising medical costs.
The money from Medicare taxes goes into a special trust. This trust pays for hospital stays, doctor visits, and home health care.
Paying these taxes is not just a rule; it’s an investment. It helps ensure people get care when they need it most. If you retire or care for an older family, this tax helps support your care.
Understanding Medicare Expenditure
The term Medicare Expenditure refers to how the government uses the funds collected through Medicare taxes. Each year, these funds are used to pay for care services that support the health of millions of Americans. This includes costs related to hospital care, outpatient services, home health care, and skilled nursing. As more people retire and live longer, the cost of care rises. This leads to higher total spending.
It is important to track Medicare Expenses so that the program can remain stable. Each year, reports are released to show how much money was spent and where it went.
High Medicare expenses are often seen as a challenge. However, it also indicates that people are receiving the necessary care. By paying these taxes, workers support these essential health programs. These taxes help cover the costs of treating illness, providing care, and saving lives.
Understanding how your tax dollars are used builds trust in the system.
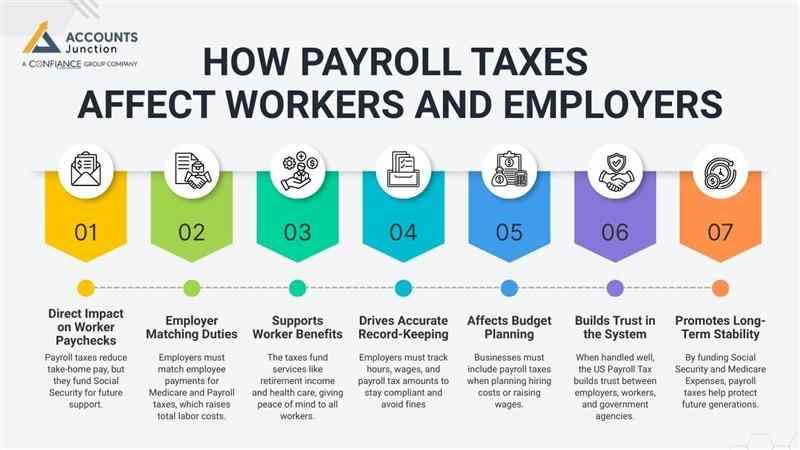
How Payroll Taxes Affect Workers and Employers
Payroll taxes affect every worker and every business. For workers, it means a small portion of their pay goes toward future support programs. For employers, it means matching that amount and staying compliant with tax rules. Here how it affects to employers to employees both.
1. Direct Impact on Worker Paychecks
- Payroll taxes reduce take-home pay, but they fund Social Security for future support.
2. Employer Matching Duties
- Employers must match employee payments for Medicare and Payroll taxes, which raises total labor costs.
3. Supports Worker Benefits
- The taxes fund services like retirement income and health care, giving peace of mind to all workers.
4. Drives Accurate Record-Keeping
- Employers must track hours, wages, and payroll tax amounts to stay compliant and avoid fines.
5. Affects Budget Planning
- Businesses must include payroll taxes when planning hiring costs or raising wages.
6. Builds Trust in the System
- When handled well, the US Payroll Tax builds trust between employers, workers, and government agencies.
7. Promotes Long-Term Stability
- By funding Social Security and Medicare Expenses, payroll taxes help protect future generations.
Tips to Stay Compliant with Payroll Tax Rules
Paying taxes can be stressful, but staying compliant is easier when you follow clear steps.Here are several helpful tips to keep you organized and compliant.
1. Keep Clear Payroll Records
- Record hours, wages, and Payroll Tax amounts to avoid errors and audits later.
2. Track Rate Updates Yearly
- Tax rates for Payroll taxes or Medicare may change. Always check updates from the IRS.
3. Use Trusted Payroll Software
- Good tools reduce mistakes and help track Medicare taxes and payment dates.
4. File and Pay on Time
- Late payments of Payroll Tax can lead to costly penalties from tax authorities.
5. Train Staff on Payroll Rules
- Make sure HR or payroll staff understand Medicare Expenditure and related payroll rules.
6. Communicate with Employees
- Tell workers what US Payroll Tax deductions mean. This builds trust and clears up confusion.
Common Payroll Tax Mistakes to Avoid
Payroll taxes can be tricky. Many small businesses and workers may make mistakes without knowing it. Some errors can lead to penalties or audits, so it helps to stay cautious.
1. Misclassifying Employees
- Treating a worker as a contractor instead of an employee may lead to missing Payroll Tax contributions. It is important to check each worker’s status carefully.
2. Late Payments
- Payroll taxes have strict deadlines. Paying late may trigger fines and interest charges. Staying organized and noting due dates can prevent mistakes.
3. Wrong Withholding Amounts
- Incorrectly calculating Social Security or Medicare taxes can cause problems. Even small miscalculations can grow over time.
4. Ignoring Rate Changes
- Payroll tax rates or wage limits can change every year. Businesses that do not update payroll systems may underpay or overpay taxes.
5. Poor Record-Keeping
- Not tracking hours, wages, or payments can make it hard to show compliance if audited. Clear, organized records are essential.
Being mindful of these mistakes may save money and stress. Awareness is the first step to smooth payroll operations.
2. How Payroll Tax May Affect Small Businesses
Small businesses often feel the weight of payroll taxes. Understanding potential impacts may help owners plan better.
1. Increased Labor Costs
- Employers must match employee contributions. This means hiring costs are higher than just the wages you pay.
2. Cash Flow Considerations
- Taxes are paid regularly, so businesses need to manage cash flow to meet deadlines. Running out of cash may create complications.
3. Record-Keeping Responsibilities
- Small businesses may struggle to maintain detailed payroll records. Mistakes may trigger audits or fines.
4. Potential for Tax Credits
- Certain small businesses may qualify for payroll tax credits. Knowing available options may reduce overall expenses.
5. Compliance Challenges
- Payroll rules may vary at federal, state, and local levels. Businesses must stay informed to avoid penalties.
Even small companies can handle payroll taxes efficiently with proper planning, software, and expert support.
3. The Future of Payroll Tax in the US
Payroll taxes are not fixed forever. They may evolve with new laws, changing demographics, or economic needs.
1. Demographic Changes
- As the population ages, Social Security and Medicare may need more funding. This could influence payroll tax rates in the future.
2. Technological Advancements
- Payroll software and automated reporting tools may simplify calculations and compliance. New tech may reduce errors and save time.
3. Policy Reforms
- Congress may adjust tax rules, contribution rates, or exemptions. Staying informed about changes is key for both employers and employees.
4. Increased Transparency
- The government may provide more detailed reporting on how tax dollars are spent. Workers may see the direct benefits of their contributions.
5. Workforce Trends
- Remote work, gig work, and flexible employment may create new payroll tax challenges. Businesses and workers may need to adapt accordingly.
Keeping an eye on trends and planning ahead may help everyone manage payroll taxes more effectively.
The US Payroll Tax is more than just a paycheck deduction. It funds care and support that people count on. Understanding how Medicare taxes work and how they support Medicare Expenses helps you see the value. With the right knowledge and support, you can handle payroll taxes with ease. Accounts Junction offers expert payroll and accounting services to help businesses stay compliant and stress-free.
FAQ
1. What is US Payroll Tax and how does it work?
- It is a federal tax on wages that funds Social Security and Medicare. Both employers and employees contribute.
2. Who is responsible for paying Payroll Taxes in the US?
- Both employees and employers must pay. Each covers a share of Social Security and Medicare taxes.
3. How much do employees pay in Social Security tax?
- Workers pay 6.2% of their wages. Employers also contribute an equal 6.2%.
4. What is the Medicare tax rate for workers?
- Employees pay 1.45% of wages, and employers match it. High earners may pay an extra 0.9%.
5. What is the Additional Medicare Tax?
- Workers earning above $200,000 may pay an extra 0.9%. Employers withhold this for qualifying employees.
6. How are Payroll Taxes calculated for hourly and salaried workers?
- Payroll Taxes are based on gross wages before deductions. Both hourly and salaried workers pay the same rates.
7. How does Payroll Tax affect take-home pay?
- It reduces net pay, but contributes to Social Security and Medicare benefits for future support.
8. What does Payroll Tax fund?
- It helps pay retirement benefits, disability income, and Medicare healthcare for older adults.
9. Are Payroll Taxes mandatory for all employees?
- Yes, most employees in the US are required to contribute under federal law.
10. How often must employers deposit Payroll Taxes?
- Firms may pay monthly, semi-weekly, or quarterly depending on size and IRS requirements.
11. What records must employers keep for Payroll Taxes?
- Hours worked, wages, tax amounts, and payment dates are critical for IRS compliance.
12. What are common Payroll Tax mistakes employers make?
- Misclassifying employees, late payments, and incorrect withholding are common errors.
13. Can independent contractors be exempt from Payroll Taxes?
- Yes, they pay self-employment tax instead, covering Social Security and Medicare themselves.
14. How do Payroll Taxes support Medicare Expenditures?
- Taxes go into a federal trust that pays for hospital, doctor, and skilled care services.
15. What happens if Payroll Taxes are paid late or incorrectly?
- Late or incorrect payments may lead to fines, interest, or IRS audits.
16. How does Payroll Tax differ for high earners?
- High earners may pay Additional Medicare Tax. Social Security taxes only apply up to a wage cap.
17. Can Payroll Taxes change over time?
- Yes, rates, wage caps, and rules may change yearly based on federal law updates.
18. How do employers match employee contributions?
- Employers calculate the same Social Security and Medicare amounts as employees and remit them to the IRS.
19. How do Payroll Taxes impact small businesses?
- They increase labor costs and require careful record-keeping for compliance and budgeting.
20. How can understanding Payroll Taxes benefit employees?
- Knowing how taxes are calculated helps workers plan finances and understand benefits like Social Security and Medicare.
