
Tax Form for Independent Contractors Explained With Real Examples
Filing taxes as an independent contractor can feel hard. The tax form for independent contractors shows all income to the IRS. Contractors handle earnings without tax being taken automatically. Many workers miss details when filing and face penalties. Knowing the right form and how to use it lowers stress.
The 1099 tax form for contractors is the main form workers receive. It helps track income from each client every year. Correctly using it ensures federal and state taxes are filed. Contractors can also claim business expenses to lower taxes. This guide explains tax forms with real examples to make them simple.
What is a Tax Form for Independent Contractors
A tax form for independent contractor work shows income earned from clients. It helps track all money made during the year for your tax form for independent contractor filing.
-
Key Purpose
It records income, even if taxes aren’t taken out. It also helps with self-employment tax when you file a tax form for independent contractor work each year.
-
Components
The 1099 tax form for contractors shows payer, contractor, total payments, and withholding. It gives the IRS details to check your income.
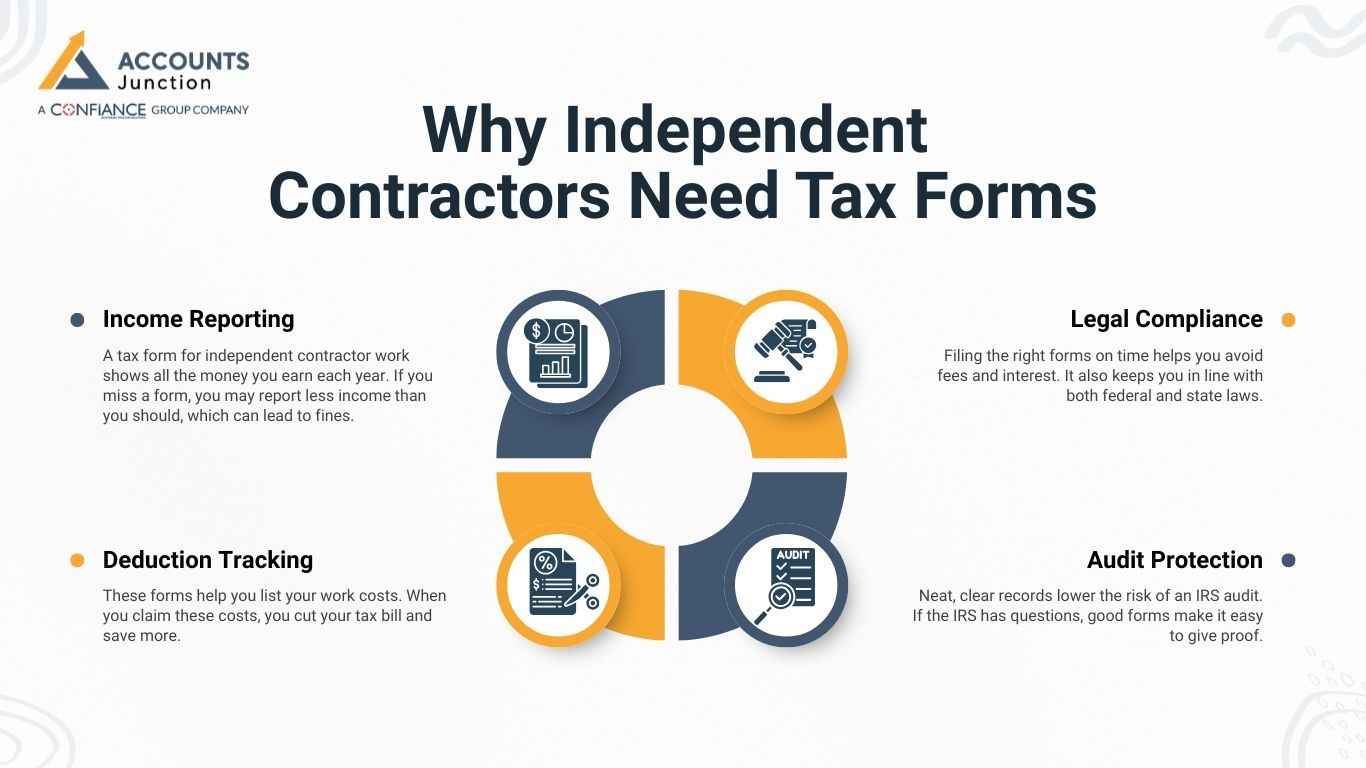
Why Independent Contractors Need Tax Forms
-
Income Reporting
A tax form for independent contractor work shows all the money you earn each year. If you miss a form, you may report less income than you should, which can lead to fines.
-
Deduction Tracking
These forms help you list your work costs. When you claim these costs, you cut your tax bill and save more.
-
Legal Compliance
Filing the right forms on time helps you avoid fees and interest. It also keeps you in line with both federal and state laws.
-
Audit Protection
Neat, clear records lower the risk of an IRS audit. If the IRS has questions, good forms make it easy to give proof.
Difference Between In-house Employees and Independent Contractors
|
Aspect |
Employees |
Independent Contractors |
|
Tax Withholding |
Taxes are taken automatically by the employer. |
Contractors pay their own taxes and submit quarterly estimated payments. |
|
Form Type |
Receive W-2 forms, which report income. |
Receive 1099 forms, which report income. |
|
Benefits |
May receive insurance, retirement plans, and other benefits. |
Manage and arrange their own health and retirement benefits. |
|
Expense Deductions |
Cannot usually deduct business expenses. |
They can deduct work costs when they file a tax form for independent contractor income. |
Understanding the 1099 Tax Form for Contractors
-
Purpose
The 1099 tax form for contractors shows payments made by clients. It ensures all independent earnings are reported to the IRS.
-
Details Included
It lists payer, contractor, total payments, and any taxes withheld. It also helps file taxes accurately and avoid mistakes.
-
Multiple Forms
Contractors often get more than one 1099 tax form for contractors in a year. All forms must be added to find total yearly income.
-
Tax Filing Use
All 1099 income must be reported on Schedule C of 1040. It also helps calculate self-employment and income tax correctly.
Common Types of 1099 Forms
- 1099-NEC
The 1099 tax form for contractors shows pay made to non-employees. It replaced the old 1099-MISC for service income.
- 1099-MISC
Reports other income like rent or awards. It may include royalties or prize payments from clients.
- 1099-K
Used for card or online payments from networks. It reports total payments processed via apps or platforms.
- 1099-INT
Shows interest income from banks or savings. It ensures all passive income is included in taxes.
- 1099-DIV
Shows dividends or investment income received. Mostly used for stocks or mutual fund earnings.
Filing Requirements for Contractors
-
Report All Income
Report all pay from 1099 on Schedule C. Small amounts must be reported to avoid IRS fines.
-
Self-Employment Tax
Use Schedule SE to find your tax due. These taxes pay Social Security and Medicare costs.
-
Claim Deductions
List all work costs tied to your tax form for independent contractor income to cut your tax bill. Right deductions help lower the tax you must pay.
-
File Federal and State Returns
Use your tax form for independent contractor income to send both federal and state forms on time. Late filing can bring fines, fees, or audits.
Real Examples of Tax Forms for Independent Contractors
-
Freelance Designer
Earned $8,000 from three clients and got 1099s. Filed Schedule C and wrote off software and supplies.
-
Delivery Service Contractor
Made $15,000 through several delivery apps this year. Reported 1099-NEC and 1099-K income, claimed car costs.
-
IT Consultant
Earned $50,000 from two clients and got 1099s. Wrote off home office, travel, and software costs.
-
Photographer Contractor
Made $12,000 from events and filed 1099s. Deducted camera gear, software, and transport costs.
Common Mistakes While Filing Tax Forms
-
Missing Income
Not reporting all 1099 pay can cause IRS fines. It can also add extra interest and late fees.
-
Wrong Form
Using the wrong tax form for independent contractor income can delay your filing. Always check that the form type matches the income earned.
-
Expense Errors
When filing a 1099 tax form for contractors, mixing personal and work costs can bring IRS issues. Keep records separate to avoid deduction mistakes or issues.
-
Late Filing
Sending in your tax form for independent contractor data late brings fines and fees. File on time to keep your taxes under control.
-
Record Confusion
Messy records make reporting hard and may cause audits. Keep invoices, receipts, and forms neat and organized.
Tips for Managing Tax Forms Effectively
-
Organize Records
Keep invoices, payments, and receipts in good order. Neat records make filing taxes faster and much easier.
-
Request Forms Early
Ask clients for 1099 forms well before deadlines. This helps ensure all income is reported correctly.
-
Track Expenses
Record costs tied to your tax form for independent contractor work to claim all deductions. Include travel, tools, and software used for work.
-
Use Accounting Tools
Software can track payments and make filing simple. It cuts mistakes and saves you time each year.
-
Professional Help
Hire a tax expert for complex income or deductions. Experts make sure forms are filed correctly and on time.
Deductions and Credits for Contractors
-
Home Office Expenses
These costs may be claimed when you file a tax form for independent contractor income. It reduces taxable income for contractors working from home.
-
Travel and Vehicle
Deduct mileage, fuel, and lodging for business travel. Keep records to support deductions in case of an audit.
-
Tools and Software
Include subscriptions, software, or equipment needed for work. Save receipts for each expense to justify deductions.
-
Meals and Communication
Deduct meals and phone costs related to business. Only include expenses directly linked to work tasks.
-
Tax Credits
Credits like the self-employment tax credit can lower taxes. Apply credits to reduce both federal and state taxes.
Estimated Taxes for Independent Contractors
-
Quarterly Payments
Pay estimated taxes every three months to avoid penalties. Divide the projected tax into four equal payments.
-
Income Calculation
Use total yearly income to estimate tax payments. Include all 1099 forms and other earnings.
-
Schedule SE Use
Calculate self-employment tax using Schedule C earnings. This covers Social Security and Medicare contributions correctly.
-
Payment Submission
Send quarterly payments with IRS Form 1040-ES. Keep payment records for verification or audits.
-
Avoid Penalties
Paying on time prevents fines and interest charges. Use each tax form for independent contractors record to avoid late tax issues.
Record-Keeping Practices for Contractors
-
Keep Invoices
Store all invoices sent and received for quick access. This helps with audits and filing taxes on time.
-
Save 1099 Forms
Save 1099 forms from clients in both formats. These forms are key for reporting income at tax time.
-
Track Receipts
Record all business costs and sort them for filing. This ensures you claim all possible tax breaks.
-
Separate Accounts
This keeps records clear when you file a tax form for independent contractor income. This keeps your records clear and avoids confusion.
-
Contracts & Agreements
Save signed contracts to confirm work and payments. These can protect you if disputes arise.
How to Correct Errors on 1099 Forms
-
Contact Client
Ask for a corrected tax form for independent contractor income if there’s an error. Make sure the corrections are done before filing.
-
IRS Submission
Send corrected forms to the IRS to avoid issues. Include both the original and corrected forms with your submission.
-
Adjust Filing
Report changes on Schedule C and pay any tax difference. Double-check to avoid mistakes or penalties later.
-
Keep Documentation
Store all correction records for audits or future use. Save emails and receipts related to the correction.
Best Practices for Independent Contractors
-
Collect W-9 Forms
Ask clients for W-9 forms before starting work. This ensures the correct details for your 1099 forms.
-
Reconcile Payments
Compare invoices with payments to spot mistakes. Fix missing or wrong payments as soon as possible.
-
Separate Accounts
Keep personal and business accounts separate for clarity. This makes tracking income, costs, and taxes easier.
-
Review Forms
Check all 1099 forms before filing taxes. Make sure names, amounts, and totals are correct.
-
Professional Help
Hire an accountant if taxes or deductions are complex. They can help with filing, deductions, and tax estimates.
The tax form for independent contractors is important for income reporting. Using the 1099 tax form for contractors helps file taxes accurately. Real examples show how contractors track income and claim deductions. Good record-keeping and timely filing lower stress and penalties.
At Accounts Junction, we help independent contractors manage taxes efficiently. We guide clients on record-keeping, filing, and claiming deductions. Our experts handle 1099 forms and quarterly tax planning. Partnering with Accounts Junction saves time, avoids mistakes, and keeps finances organized. Using our services lets contractors focus on work without tax worries.
FAQs
1. Who must receive a tax form for independent contractors?
- All who earn over six hundred dollars must get a tax form for independent contractor reporting. Clients must provide forms by January thirty-first each year.
2. Can I file taxes without a 1099 form?
- Yes, report all income earned to avoid IRS issues. Keep records of payments if no form is received.
3. Are deductions allowed for independent contractors?
- Yes, business expenses reduce taxable income every year. Maintain receipts for verification if the IRS audits records.
4. What if I received multiple 1099 tax forms for contractors?
- Add all income and report the total on Schedule C. Include every form to ensure accurate reporting to the IRS.
5. How can I avoid mistakes while filing the 1099 Form?
- Keep organized records and review forms before submitting. Check amounts, client details, and expenses carefully.
6. Is an estimated tax payment mandatory for independent contractors?
- Yes, quarterly payments avoid penalties and interest charges. They prevent large tax bills at the end of the year.
