
Detailed Tax Guide for Traders
Trading may look easy from the outside, but it feels complex inside. Many traders study charts daily but often forget about tax rules. Taxes may sound dull, yet they control how profits stay secure. A proper Tax Guide for Traders may turn stress into a clear understanding. Knowing how taxes work can protect your income from sudden loss. It can also stop penalties and guide smarter money planning. In trading, the right timing and the right tax plan both matter. A small error with taxes may lead to big problems later.
This guide helps traders at all stages deal with taxes better. From fast trades to long-term holds, each trade affects the outcome. Many traders realize too late how taxes change the total yearly profit. That is why a Tax Guide for Traders is worth real attention. It breaks tricky tax terms into short, plain, and clear lines. By learning these points, traders can file smoothly and plan ahead. Tax planning may not make one rich, but it builds a strong foundation. Let’s explore how smart steps can help traders manage taxes better.
The Role of a Tax Guide for Traders
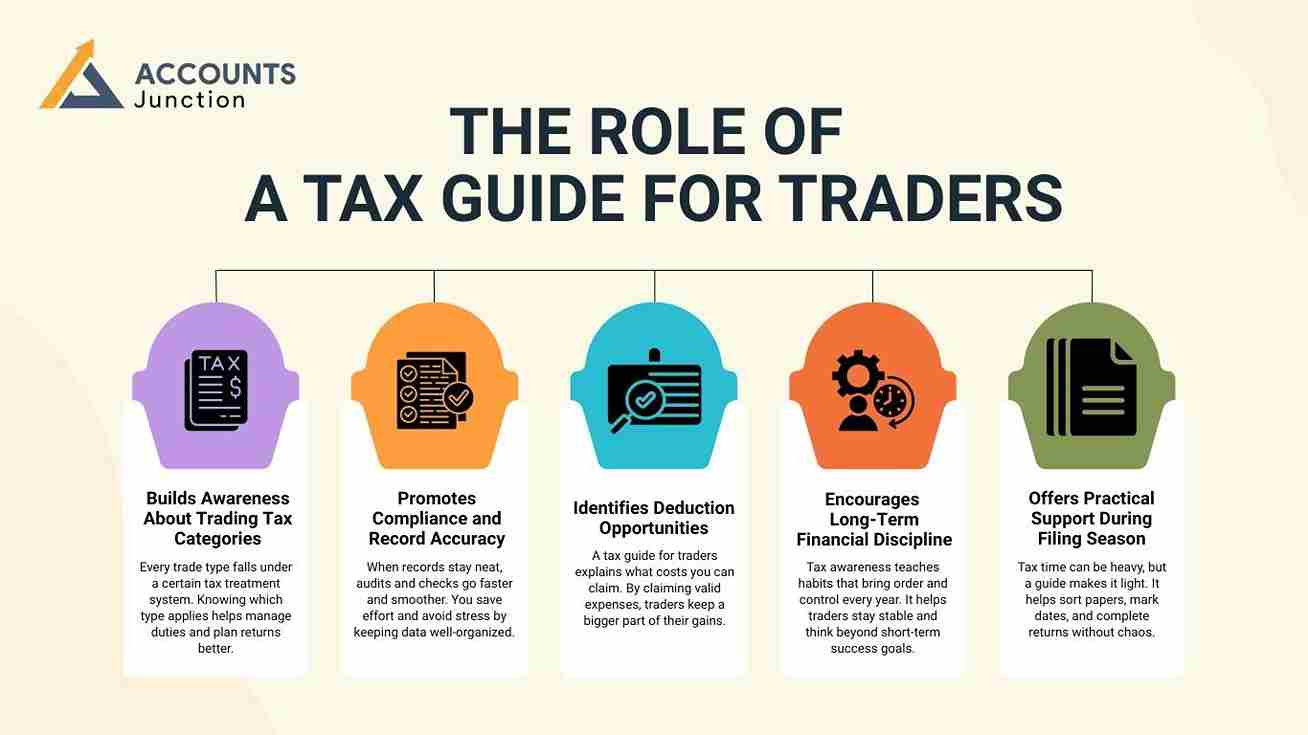
A trader with tax knowledge may save more money over time. This tax guide for traders offers clear help for filings and reports. It serves as a tool that brings order, control, and calmness. Both new and seasoned traders can benefit from planned tax steps. Even small actions can help avoid confusion and reduce yearly risk. Below are key reasons why this guide may change your approach.
-
Builds Awareness About Trading Tax Categories
Every trade type falls under a certain tax treatment system. Knowing which type applies helps manage duties and plan returns better.
-
Promotes Compliance and Record Accuracy
When records stay neat, audits and checks go faster and smoother. You save effort and avoid stress by keeping data well-organized.
-
Identifies Deduction Opportunities
A tax guide for traders explains what costs you can claim. By claiming valid expenses, traders keep a bigger part of their gains.
-
Encourages Long-Term Financial Discipline
Tax awareness teaches habits that bring order and control every year. It helps traders stay stable and think beyond short-term success goals.
-
Offers Practical Support During Filing Season
Tax time can be heavy, but a guide makes it light. It helps sort papers, mark dates, and complete returns without chaos.
Categories of Traders for Tax Treatment
Traders do not all fall into the same tax group. A tax guide for traders clears this by explaining each trader type. Tax laws treat casual investors and full-time traders very differently.
-
Occasional or Part-Time Traders
They trade rarely, often to earn side income apart from their main work. Their profits fall under capital gains rather than normal income tax.
-
Active Individual Traders
They trade often, earning through short-term market price changes daily. Their income usually counts as business profit and not investment gain.
-
Professional Full-Time Traders
They depend mainly on trading as a steady business income source. They may claim higher deductions for costs tied to trading work.
-
Proprietary or Institutional Traders
These trade on behalf of clients or groups with strict rules. They file taxes under standard corporate or institutional systems yearly.
-
Automated and Algorithmic Traders
They trade using software and systems built for fast data decisions. These also fall under business income, based on regular operations.
Common Types of Taxes Traders Encounter
Taxes vary with trade type, trade count, and time frame. A good tax guide for traders lists these main taxes in detail.
-
Capital Gains Tax
This applies when you sell assets for more than the purchase value. Short-term gains get taxed higher rate, while long-term gains face lower rates.
-
Income Tax on Trading Profits
If trading is your main job, profits become taxable as income. You must record all earnings clearly and file them on time.
-
State and Local Taxes
Each state may charge extra based on where you live or work. Checking rates early avoids last-minute surprises during the final filing season.
-
Self-Employment Tax for Professionals
Professional traders may owe this if they trade as individuals. It covers both income and contribution duties to social funds.
-
Securities Transaction or Duty Taxes
Some trades include tiny duty costs on every single transaction. These can be claimed as expenses when filing your yearly taxes.
Deductible Expenses in a Tax Guide for Traders
Expenses linked to trading may lower your total taxable amount. Knowing which ones qualify keeps filings clean and profit margins stronger. A tax guide for traders can help list these in a simple form.
-
Trading Software and Data Platforms
Subscription costs for real-time charts or market tools are deductible. They are key for decision-making and daily trading operations.
-
Internet and Utility Expenses
Your internet and power bills partly count as work-related costs. If used mainly for trading, you can include them in deductions.
-
Office Space or Home Office Deductions
If you use space for trading work, claim a portion as an expense. Keep receipts and calculate only for the area used for business.
-
Education, Research, and Skill Development
Training, books, or workshops tied to trading may be deductible. They show investment in skill, which tax laws often encourage.
-
Professional and Advisory Fees
Tax filing or accounting help counts as a valid business service cost. A solid tax guide for traders stresses proof for each claimed service.
Importance of Organized Record Keeping
Records keep your tax story clear, accurate, and ready for review. Missing papers may cost you deductions or invite audit issues. Proper files show your professionalism and keep tax filings stress-free.
-
Maintain Clear Trade Logs
Note every trade with date, cost, and gain details included. Use simple software that auto-tracks for easier monthly reviews.
-
Preserve Broker and Platform Statements
These show monthly profits, losses, and paid commission amounts. They act as core proof when explaining income to tax officers.
-
Separate Personal and Business Expenses
Mixing both can confuse records and cause unnecessary tax problems. Keep two accounts so your trade costs stay clean and clear.
-
Keep Records of Fees and Commissions
Brokerage and exchange fees often add up during busy trade seasons. Listing them ensures fair deductions and balanced financial summaries.
-
Regularly Update Data and Reconcile Accounts
Check and update books weekly to spot early mismatches or errors. It saves time and stress later when you prepare your returns.
Common Reporting and Accounting Methods
Reporting style shapes how your profit and loss are recorded. A tax guide for traders explains which systems may suit your case.
-
Cash Basis Accounting
You record income only after it reaches your bank account. It’s easy for smaller traders with fewer trades per year.
-
Accrual Basis Accounting
Here, you record profits when trades close, not when paid. It gives a full picture of yearly performance and flow.
-
Mark-to-Market Accounting
It counts unrealized gains or losses at year-end each time. This helps large traders simplify tracking across complex portfolios.
-
FIFO or LIFO Evaluation
You decide which stock counts first, oldest or newest sold. Choose one way and keep it the same for every tax filing.
-
Hybrid Methods for Flexibility
Mixing systems can help balance reporting for better clarity. Use expert help to stay within approved and legal standards.
Managing Taxes Efficiently as a Trader
Handling taxes well means more control and more peace yearly. A tax guide for traders lists simple actions to make it easier.
-
Timing of Sales and Purchases
Shift trade dates slightly to balance gains within lower brackets. Smart timing can lower yearly tax outflow without breaking rules.
-
Use of Loss Offsetting
You may cut taxable gains using earlier losses from other trades. This reduces what you owe and improves your overall record.
-
Investing Within Retirement Accounts
Some accounts allow tax-free or delayed taxation on trade profits. Using them grows wealth faster with fewer annual tax payments.
-
Claiming Eligible Business Expenses
Recording all valid costs ensures each one counts toward savings. This helps reduce the total amount payable at the end.
-
Consulting a Tax Expert Regularly
Yearly checks with experts help find gaps or fresh deductions. Tax rules change often, so staying updated is always wise.
Mistakes Traders Should Avoid
Even smart traders may face losses from simple tax mistakes. A tax guide for traders points out errors that you can avoid.
-
Ignoring Detailed Record Keeping
Missing notes or slips may cause loss of key deduction chances. Always store digital and paper copies for all major transactions.
-
Confusing Investor and Trader Classifications
The wrong tag can lead to paying extra tax without reason. Identify your role first to enjoy proper tax relief benefits.
-
Forgetting to Report Small Fees
Minor costs like data fees often get ignored, but still count. Adding them up can raise your valid deductible total easily.
-
Filing Late or Missing Deadlines
Late filing attracts penalties that can cut your net profit. Mark all dates early and submit returns before closing dates.
-
Relying Solely on Generic Software
Software tools help, but they can miss specific trading tax rules. Manual review by experts ensures you file without costly mistakes.
Effective trading is not just about numbers or screen time spent. It also means staying aware of your tax duties and rules. A smart tax guide for traders can turn confusion into control. With clean records and wise expense plans, filing becomes smooth. Better tax handling means more peace and more yearly savings. Tax awareness may not raise returns overnight, but it keeps profits steady. Stay alert, keep learning, and let smart planning grow your success. Accounts Junction provides professional accounting and tax services tailored to traders and investors, ensuring every transaction is accurately recorded and reported. We have certified experts who stay updated with the latest rules and regulations, giving your trading business a solid financial foundation. Partner with us.
FAQs
1. What taxes do active traders usually pay?
- Active traders pay income tax and self-employment tax.
- They should also check state and local taxes every year.
2. How is the capital gains tax applied to traders?
- Gains from sold assets are taxed as short-term or long-term.
- How long you hold affects whether the rate is high or low.
3. Can trading losses offset profits for tax purposes?
- Yes, losses can reduce taxable gains under set rules.
- Unused losses may also be used in future tax years.
4. Are trading software and tools tax-deductible?
- Yes, software or tools used mainly for trading qualify.
- Keep bills and receipts to claim them correctly each year.
5. Can home office costs be claimed by traders?
- Yes, a workspace used for trading can be deductible.
- Only the part used for trading counts, not personal use.
6. Should traders use mark-to-market accounting?
- Mark-to-market can make yearly gain or loss tracking easier.
- It also shows unrealized profits and losses for each tax year.
7. How do professional and casual traders differ in taxes?
- Professional traders get more deductions and different income rules.
- Casual traders often pay regular capital gains tax on sales.
8. Are advisory and accounting fees deductible for traders?
- Yes, fees for tax help or trading advice can be claimed.
- This includes bookkeeping, accounting, and legal costs tied to trading.
9. How often should traders track and organize trades?
- Records should be kept up-to-date for accurate tax reporting.
- Frequent tracking helps calculate gains, losses, and deductions correctly.
10. Can traders deduct educational courses related to trading?
- Yes, courses that improve trading skills can be deducted.
- Only costs directly linked to trading education are allowed.
11. Are cryptocurrency trades taxed differently for traders?
- Crypto trades follow capital gains rules and need proper records.
- Each sale or exchange must be reported to stay compliant.
12. How do traders claim margin interest as an expense?
- Interest paid on borrowed funds for trades may be deductible.
- Keep clear records showing loans are used only for trading.
13. What records must traders keep for tax filing?
- Keep trade logs, statements, fees, and documents for all trades.
- Good records make audits and yearly filing much easier.
14. Can short-term and long-term holdings be taxed differently?
- Yes, short-term trades usually face higher rates than long-term.
- Long-term holdings may lower the tax you need to pay.
15. How do traders handle state and local taxes?
- Check local rules as state taxes add to federal obligations.
- Filing early and understanding laws can avoid unexpected fines.
16. Can trading losses be carried forward to future years?
- Yes, unused losses can offset profits in future years.
- Carry-forward rules may differ by country, so verify local laws.
17. Should traders consult a tax expert regularly?
- Yes, experts help avoid mistakes and make more deductions.
- Regular checkups keep you updated on changing tax rules.
18. What are common mistakes traders make during tax filing?
- Missing records, wrong classification, and overlooked expenses are common.
- Failing to track deductions or timing trades can increase tax owed.
19. Can traders deduct transaction fees and broker commissions?
- Yes, commissions and transaction costs paid to brokers are deductible.
- Track all fees carefully to claim the full allowable amount.
20. Are foreign trades subject to additional taxes?
- Yes, international trades may need reports to other tax authorities.
- Keeping records helps avoid penalties and ensures proper compliance.
