
Common Tax Mistakes to Avoid in Hong Kong: Key Tips on Taxation and Tax in Hong Kong
Taxation in Hong Kong is known for its simplicity and business-friendly environment. The city follows a territorial tax system, meaning only income earned within Hong Kong is subject to tax. Hong Kong's tax system is regulated by the Inland Revenue Department. It offers tax efficiency, making it an attractive destination for businesses and individuals. However, understanding the rules surrounding tax in Hong Kong is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid financial penalties.
Common Hong Kong Tax Mistakes Made by Individuals and Businesses
Hong Kong offers a simplified tax structure. Still, individuals and businesses frequently make tax mistakes. These errors can result in unnecessary liabilities and penalties. Common mistakes frequently observed are:
- Failure to Declare All Income – Many businesses make mistakes in tax in Hong Kong by assuming offshore income is automatically exempt without proper documentation.
- Late Submission of Tax Returns – Tax returns must be filed on time. Late submissions result in fines. The Inland Revenue Hong Kong can also impose legal consequences.
- Misclassification of Income – Incorrectly categorizing income sources can lead to miscalculations and potential audits.
- Overlooking Deductions and Allowances – Many taxpayers fail to take advantage of available deductions, such as business expenses and depreciation.
- Ignoring Provisional Tax Payments – Not planning for provisional tax can cause cash flow problems when large tax payments are due.
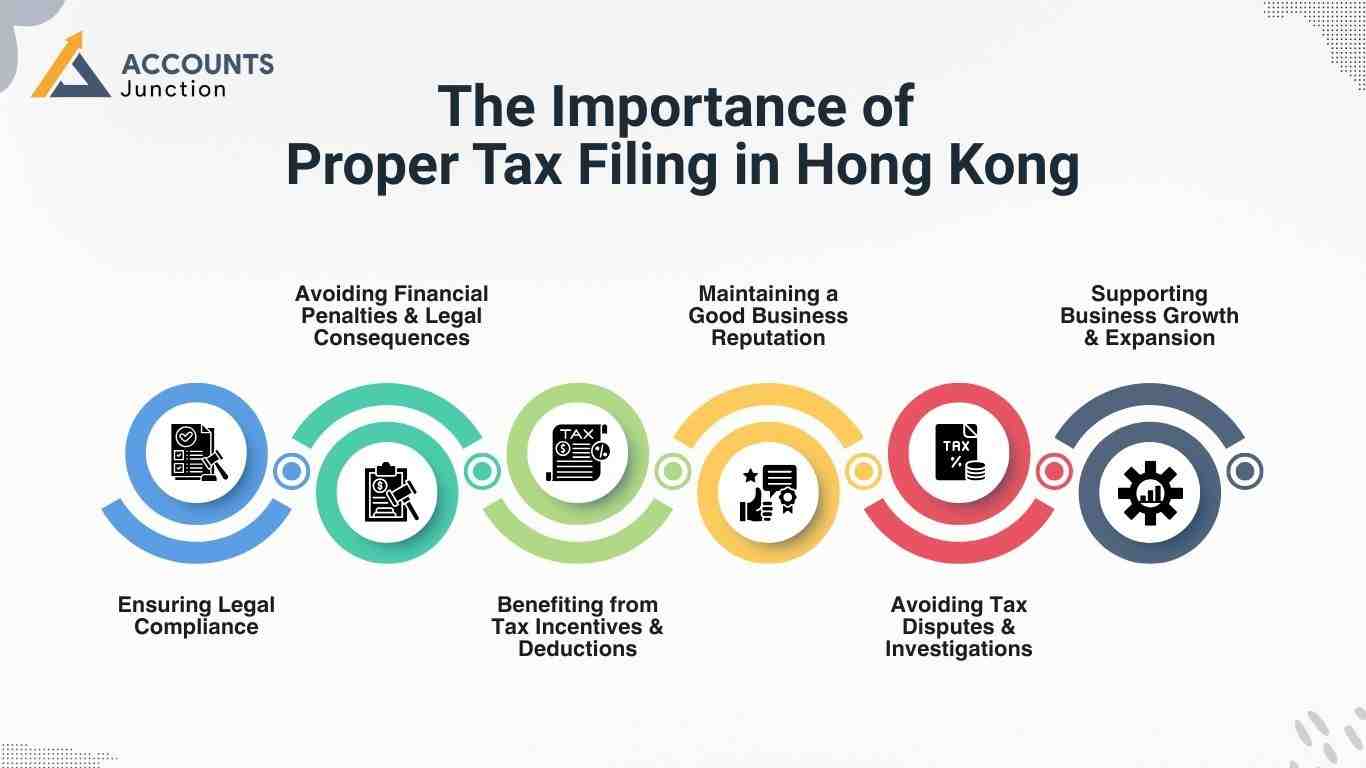
The Importance of Proper Tax Filing in Hong Kong
1. Ensuring Legal Compliance
Mandatory Requirement – Businesses and individuals must file tax returns as per the Inland Revenue Ordinance (IRO).
Avoiding Penalties – Late or incorrect filings lead to fines, interest charges, or legal action.
Audit Preparedness – Proper filing ensures accurate records in case of a tax audit by the Inland Revenue Department (IRD).
2. Avoiding Financial Penalties & Legal Consequences
Late filing may result in fixed penalties (HKD 1,200 to HKD 10,000).
Severe cases can lead to court prosecution and higher fines.
Consistently incorrect filings may trigger IRD investigations.
3. Benefiting from Tax Incentives & Deductions
Profits Tax Exemptions – Offshore businesses can apply for tax exemption on foreign-sourced income.
Allowable Deductions – Businesses can claim rent, salaries, business expenses, and depreciation to reduce taxable income.
Personal Tax Benefits – Individuals can claim deductions on education expenses, home loan interest, and retirement contributions (MPF).
4. Maintaining a Good Business Reputation
Ensures compliance with banks, investors, and regulators.
Essential for securing business loans, investments, or IPO opportunities.
Non-compliance may affect government licenses or contracts.
5. Avoiding Tax Disputes & Investigations
Proper tax filing reduces the risk of tax evasion allegations.
Maintain clear financial records to avoid disputes with IRD.
Helps in smooth tax audits by providing accurate reports.
6. Supporting Business Growth & Expansion
Ensures smooth cross-border transactions by complying with international tax treaties.
Helps businesses take advantage of Hong Kong’s low corporate tax rate (8.25% - 16.5%).
Enables strategic tax planning for long-term profitability.
How to Avoid Penalties and Late Fees on Taxes in Hong Kong
To prevent unnecessary financial penalties and late fees, businesses and individuals should follow these best practices for tax in Hong Kong:
- Stay Informed – Keep up to date with the latest tax regulations and deadlines issued by Inland Revenue Hong Kong.
- Use Accounting Software – Leverage modern tools to track income, expenses, and tax obligations efficiently.
- Seek Professional Assistance – Hiring tax professionals can ensure accuracy and timely submissions.
- File Provisional Taxes on Time – Avoid sudden cash flow burdens by preparing for provisional tax payments in advance.
- Maintain Proper Documentation – Keep records of all income, expenses, and business transactions for audit purposes.
Best Practices for Managing Taxation in Hong Kong Efficiently
1. Ensure Timely Tax Filing & Compliance
Meet Deadlines – File Profits Tax, Salaries Tax, and Property Tax returns before the IRD deadlines to avoid penalties.
Use Extended Deadlines – Apply for the Block Extension Scheme if eligible.
Submit Employer’s Returns – Accurately report employee salaries and benefits on IR56B forms.
2. Maintain Proper Financial Records
Keep Accurate Books – Maintain financial statements, invoices, and tax-related documents for at least 7 years.
Separate Personal & Business Finances – Use a dedicated business bank account for transactions.
Reconcile Accounts Regularly – Ensure tax-related expenses and revenue are correctly recorded.
3. Leverage Tax Deductions & Incentives
Claim Allowable Deductions – Maximize savings under the tax in Hong Kong rules by including rents, salaries, marketing, and depreciation. Use MPF Contributions – Mandatory Provident Fund (MPF) contributions are tax-deductible.
Utilize R&D Tax Incentives – Qualifying R&D expenditures can receive super deductions of 300% - 400%.
4. Optimize Corporate Tax Planning
Utilize Offshore Tax Exemptions – Income derived outside Hong Kong may qualify for zero tax under the territorial tax system.
Structure Business Effectively – Consider setting up holding companies or subsidiaries for tax efficiency.
Plan Dividend Distribution – Hong Kong has no withholding tax on dividends, offering tax-saving opportunities.
5. Stay Updated on Tax Laws & Regulations
Monitor IRD Announcements – Keep track of new tax laws, regulations, and policy changes.
Comply with BEPS 2.0 & Transfer Pricing Rules – Ensure proper documentation for cross-border transactions.
Adapt to Digital Tax Filing – Use the IRD’s eTAX system for online filing and assessments.
Understanding Hong Kong’s Territorial Tax System
Hong Kong uses a territorial tax system, which is a big advantage for businesses and individuals. Only income earned in Hong Kong is subject to tax in Hong Kong. Income from outside Hong Kong, such as foreign sales or overseas investments, may not be taxed if proper records are kept.
Key Points:
- Profits earned outside Hong Kong may be exempt from tax in Hong Kong if there is clear proof of where the income came from.
- Keep all contracts, invoices, and bank records to show where money comes from.
- Misunderstanding the rules can lead to overpaying taxes or being audited by the Inland Revenue Department (IRD).
- Even simple errors in documenting offshore income can trigger delays or additional checks by the IRD.
Common Tax Filing Mistakes for SMEs
Small and medium-sized businesses often face challenges in filing tax in Hong Kong correctly. Mistakes can lead to penalties and extra work.
Typical Mistakes:
- Poor record-keeping of business income and costs.
- Misunderstanding which business costs can reduce taxable income.
- Treating owner withdrawals as salaries instead of drawing from profits.
- Forgetting to file provisional tax can cause cash flow problems.
Solution:
- Set up a clear and simple accounting system.
- Review records regularly to check for mistakes.
- Work with a tax professional to ensure filings comply with tax in Hong Kong.
- Keep all receipts and invoices for at least seven years for audit purposes.
Importance of Transfer Pricing Documentation
Companies doing business across borders must follow rules for transfer pricing. This ensures they comply with tax in Hong Kong and avoid disputes with the IRD.
Key Points:
- Shows that transactions with related parties are fair and correct.
- Prevents changes to tax bills during audits.
- Helps meet international rules like BEPS 2.0.
- Keeps your business safe from penalties and disputes in other countries.
Using Double Taxation Agreements (DTAs)
Hong Kong has agreements with over 40 countries to avoid double taxation. Using these agreements wisely can reduce tax liabilities in Hong Kong and improve cash flow.
Benefits of DTAs:
- Lowers withholding taxes on dividends, interest, and royalties.
- Clarifies which country can tax certain income.
- Lets you claim foreign tax credits against tax in Hong Kong.
- Helps businesses expand globally while staying compliant.
Digital Tools for Efficient Tax Filing
Digital tools make filing taxes in Hong Kong faster and reduce mistakes. They also help track deadlines and payments.
Best Practices:
- Use the IRD eTAX system for online filing and tax payments.
- Link your accounting software to generate tax reports automatically.
- Set reminders for filing deadlines to avoid late fees.
- Keep digital copies of all records for easy access during audits.
- Use cloud-based systems to track income and expenses in real-time.
Hong Kong offers a business-friendly tax system. Ensuring proper compliance with tax in Hong Kong is essential for businesses. This avoids penalties and maximizes tax efficiency. Businesses and individuals should understand common tax mistakes. They must also stay compliant with Inland Revenue Hong Kong regulations. Implementing best practices allows for smooth taxation management. Accounts Junction offers professional tax management. This service ensures a hassle-free experience. Clients can then concentrate on their core business. Financial stability is also maintained.
Accounts Junction offers tax services in Hong Kong. We know local tax rules and keep up with IRD updates. We file taxes on time and help plan to lower tax costs while staying within the law. Our team helps with audits, disputes, and international tax rules. We use modern tools to make processes fast and easy. Partner with Accounts Junction for simple and clear tax solutions.
FAQs
1. What is the tax system in Hong Kong?
- Hong Kong taxes only income earned in the city.
2. Who must file tax returns in Hong Kong?
- People and businesses with Hong Kong income must file yearly returns.
3. What taxes apply in Hong Kong?
- Profits Tax, Salaries Tax, and Property Tax are the main taxes.
4. When should I file my tax return in Hong Kong?
- Individuals file by June; businesses by April, unless extended.
5. What is provisional tax in Hong Kong?
- It is an advance payment based on last year’s tax.
6. Is offshore income taxable in Hong Kong?
- Foreign income may be exempt if documented correctly.
7. What penalties exist for late tax filing on tax in Hong Kong?
- Fines range from HKD 1,200 to 10,000; legal action may follow.
8. How can businesses avoid penalties in Hong Kong?
- File on time, keep records, and plan for provisional tax.
9. Can businesses use software for Hong Kong tax?
- Yes, it tracks income, costs, and deadlines easily.
10. How can companies plan corporate tax?
- Use offshore exemptions, claim deductions, and plan business structure.
11. Are dividends or foreign income taxed in Hong Kong?
- Dividends are not taxed; foreign income may be exempt.
12. Why stay updated on Hong Kong tax rules?
- To comply, avoid fines, and use all allowed deductions.
13. Can foreign companies be taxed in Hong Kong?
- Only income sourced in Hong Kong is taxable for foreign businesses.
14. How does Hong Kong taxation treat business expenses?
- Business costs are deductible to lower taxable profits under Profits Tax.
15. Are rental incomes taxed in Hong Kong?
- Yes, rental income is subject to Property Tax in Hong Kong.
16. Do startups benefit from Hong Kong tax incentives?
- Yes, startups can claim R&D deductions and other allowable expenses.
17. How does Hong Kong tax part-time or freelance income?
- All income earned in Hong Kong, including freelance work, is taxable.
18. Can expatriates claim tax relief in Hong Kong?
- Yes, eligible expatriates may claim deductions under the Salaries Tax rules.
19. How does Hong Kong taxation handle capital gains?
- Capital gains are generally not taxed in Hong Kong.
20. Are profits from online businesses taxed in Hong Kong?
- Yes, profits sourced in Hong Kong are subject to Profits Tax.
21. How does Hong Kong taxation treat employee benefits?
- Employee benefits are considered part of taxable salary income tax.
22. Can Hong Kong businesses defer tax payments?
- Provisional tax planning can help manage cash flow and defer payments.
